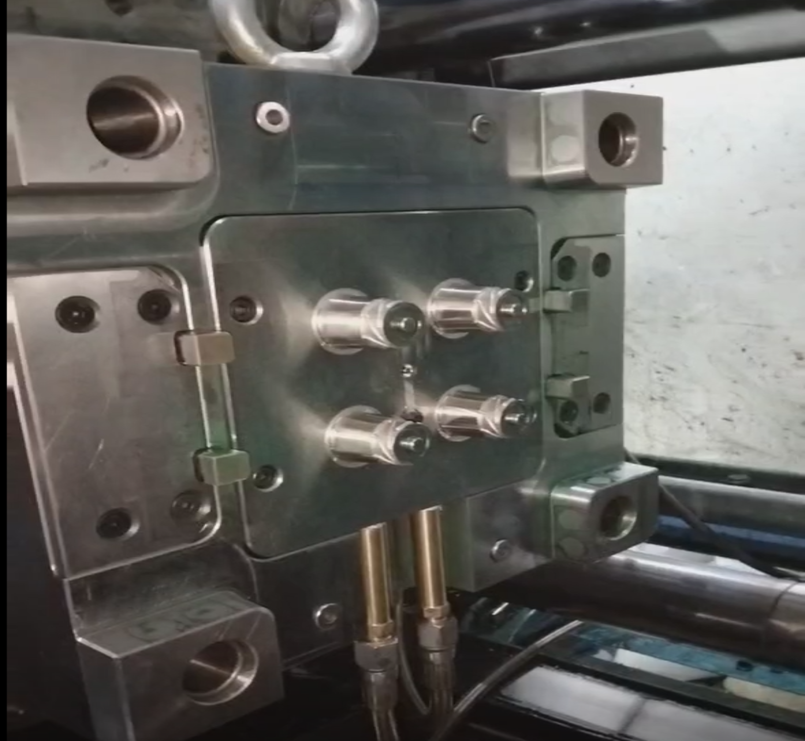
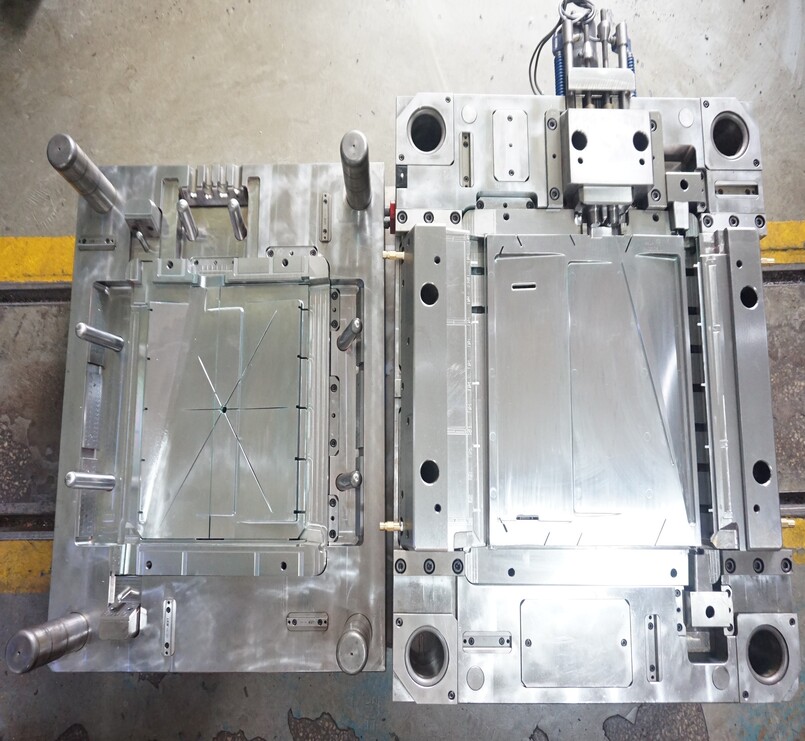
Plastic Threading mold
- Home
- Plastic Threading mold
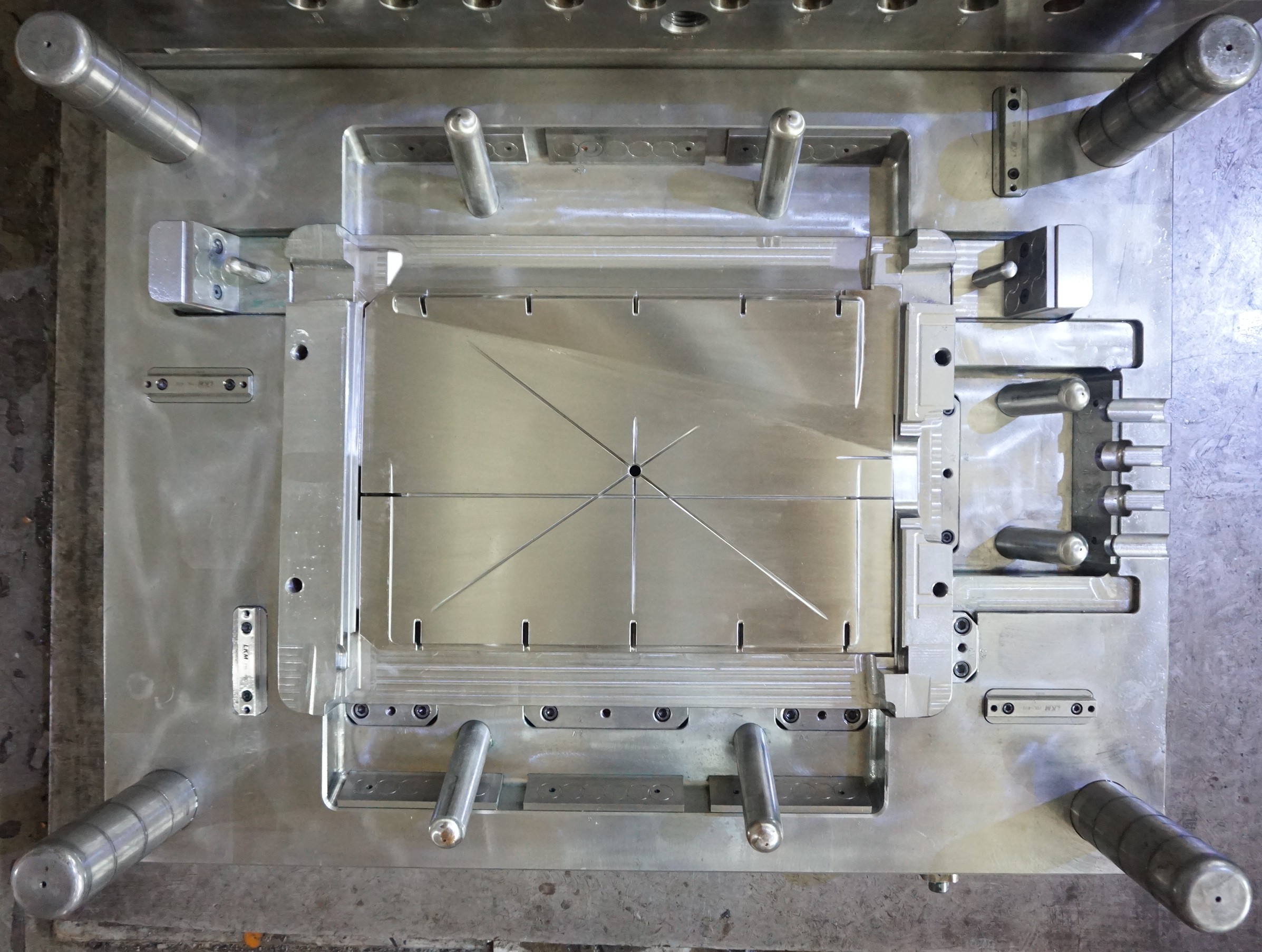
What is plastic threading mold?
When a plastic molded product has an internal thread (spiral), there is an inverted concavity and the molded product cannot be removed from the cavity by the normal demolding method. The main methods of automatic mold release for products with internal threads are as follows.
. Screw out internal threads
. Hydraulic motor;
. Cylinder with rack and pinion
. Front and rear mold parting
. Manual Release cores,
. Collapsible cores;
What should I pay attention to when designing a thread forming mold?
- When designing a thread forming die, consider the type of drive according to the type of stop and the number of threads of the product.
- Take the same modulus for the drive gear, usually 1.5, 2, 2.5 standard straight teeth with a pressure angle of 20 degrees. Available 738, NAK80, etc. steel after heat treatment, wire cutting to make. The transmission ratio is usually 2 to 3.5. 3.
- Direction of rotation of the threaded core. If the product thread is right-handed. Then the threaded core is rotated clockwise. This determines the direction of rotation of the drive mechanism.
Threaded products application:
– Automotive parts
– Electrical appliances
– Bottle caps
– Machinery
– Toys
– Construction parts
– Furniture parts
What are the ways to get to unscrewing in process threaded molded product by injection molding?
1. Non-rotating release the thread
- Inserting threaded cores:Forced de-threading: This type of unscrew product has a simple mold structure and is usually used for products that do not require high precision. Its main principle is to release the thread through the elasticity of the plastic. This is generally for tough plastics (PE, PP, etc.) with semicircular shallow coarse teeth.
- Manual unscrewing: The threaded core is unthreaded along with the product, and the product is separated from the threaded core by hand or simple tools outside the machine tool. This kind of mold structure is simple, but it needs many threaded cores and to preheat, easy to manufacture, but labor intensive and low production efficiency.
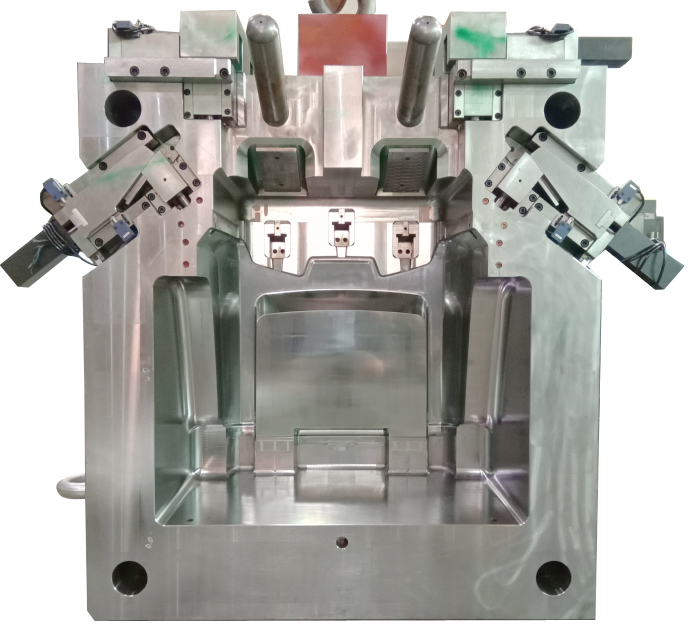

2. Unscrew by motor drive
- The hydraulic motor drives the sprocket through the chain, so as to exit the product.
- Motor drive cannot be accurately positioned, so the tooth shaft cannot move up and down.
- Motor, chain, sprocket, bearing… There are standard parts for sale.
This way commonly used in products with more threads. The peripheral stop case. (Because the motor rotation can not be accurately positioned. Therefore, it is not suitable for threaded core downward movement out of the product) motor usually with the chain, sprocket drive.
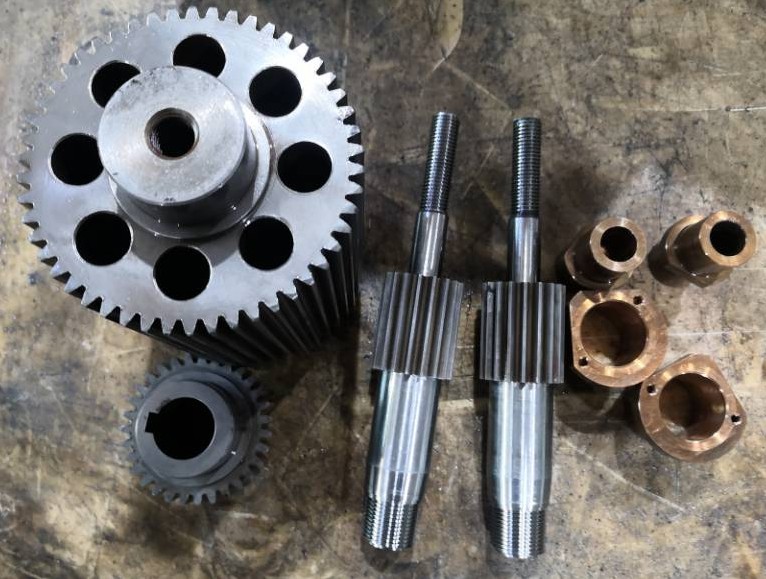
3. Unscrew by cylinder with rack and pinion out of the internal thread
- Rack, gear modulus m is often taken 1.5, 2, 3 … The center distance between each two teeth of the rack is 3.14 xm
- The stroke of the cylinder is: z1 is the number of teeth of the gear on the threaded shaft. N is the number of turns of the thread on the product. I is the transmission ratio of the two intermediate gears.
- The threaded shaft can be moved up and down during the working process.
- The threaded sleeve can be made of copper alloy.
The internal thread of the cylinder with rack and pinion is suitable for the case where the number of threads is small (such as 2 to 4 teeth. …) If the number of threads is large, the transmission ratio must be larger, which will cause the die blank to become larger. If the transmission ratio is small, the cylinder stroke is too long.
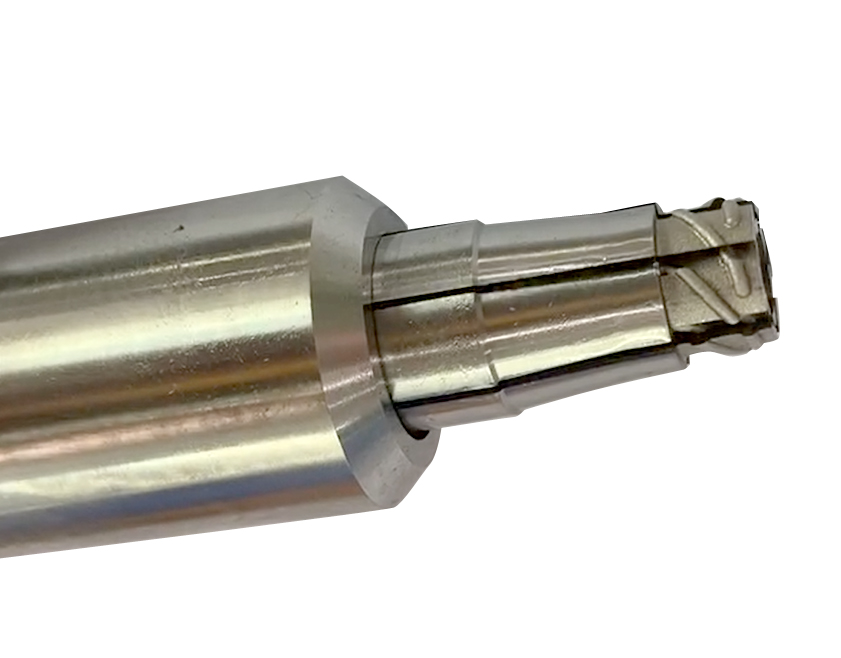
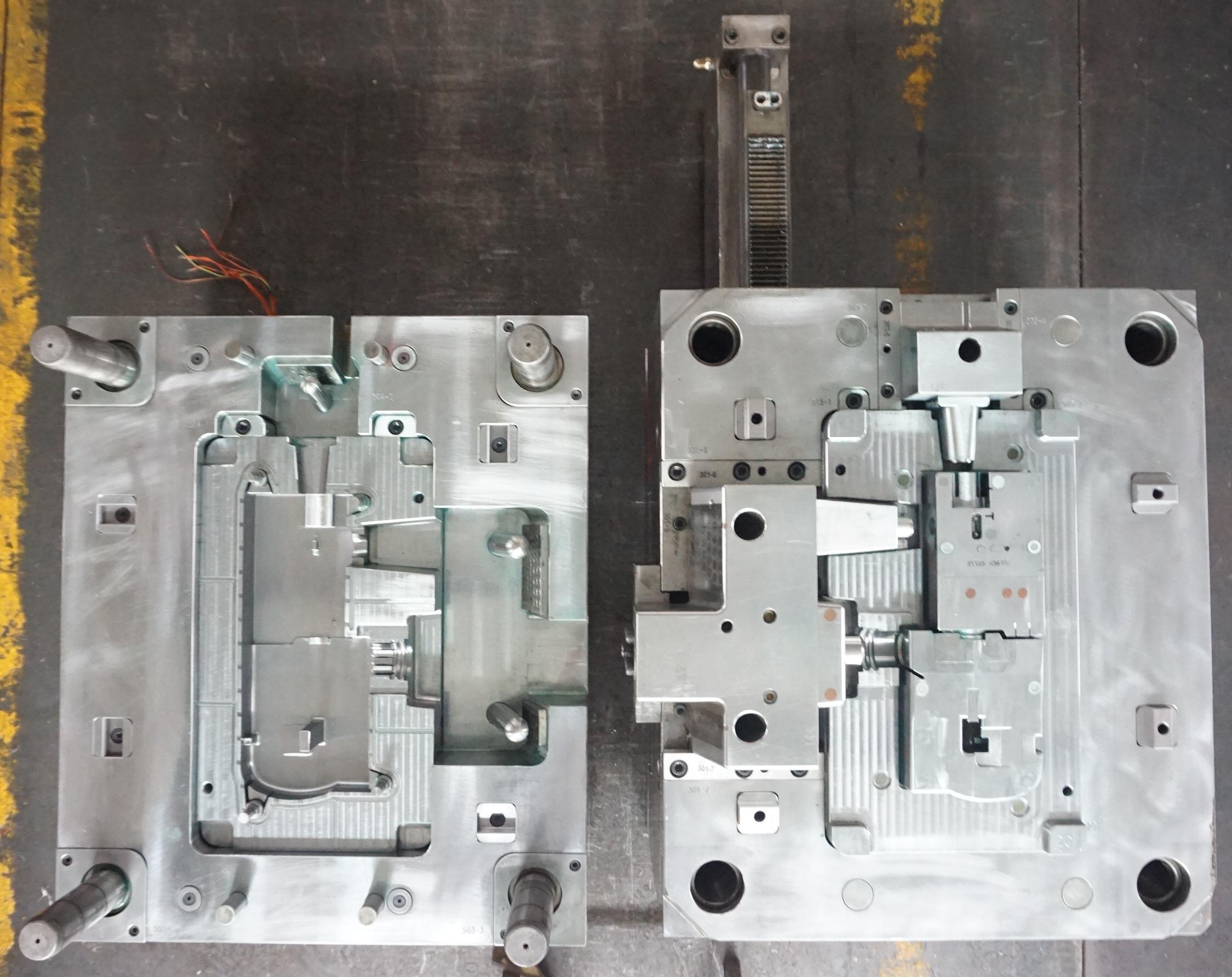

4.Unscrew with collapsible cores
Collapsible cores can be used to deflate the split section forming the threaded part by moving the push tube back and forth, thus removing the threaded part, DME or HASCO collapsible insert standard parts, suitable for products with a large number of internal thread teeth, or the whole turn has a reverse buckle. Muyoung has the resources to make precision collapsible cores but the price is lower than DME or HASCO. We are ready for you to inquire
Muyoung proceeds with the mold design by judging the suitability of these mold structures based on the customer’s need to use the function of the thread, and then determines exactly which structure to use before proceeding with the mold design. If the structure of the threaded part is not designed carefully enough, it may not move well or the threaded part may not be pulled out as expected, so it is important to refer to the skilled thought design and the existing technical examples.



